SD-WAN
SD-WAN overview
SD-WAN stands for software-defined wide area network (or networking). A WAN is a connection between local area networks (LANs) separated by a substantial distance—anything from a few miles to thousands of miles. The term software-defined implies the WAN is programmatically configured and managed. So, it can be easily adapted to meet changing needs.
How Does SD-WAN Work?
There are several characteristics that are generally attributed to SD-WANs. Let’s walk through them and learn more about the way SD-WAN works.
Centralized control
The primary means of control in an SD-WAN is centralized. It often resides in a SaaS application, running on a public cloud. Control is decoupled from the hardware to simplify network management and improve the delivery of services. SD-WAN appliances (and virtual appliances) follow operational rules passed down from the central SD-WAN controller. This greatly reduces or eliminates the need to manage gateways and routers on an individual basis.
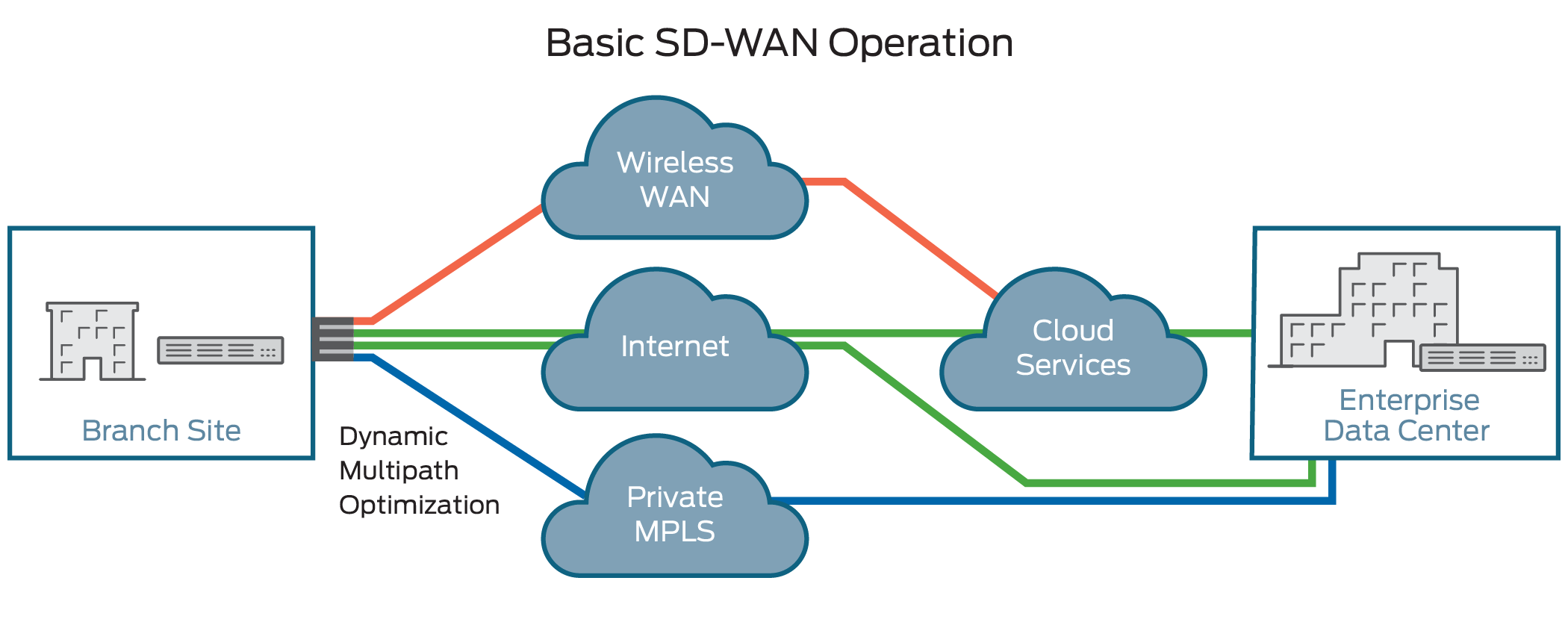
Multi-connection, Multi-transport
SD-WAN gateways support hybrid WAN, which implies that each gateway can have multiple connections using different transports—MPLS, broadband Internet, LTE, etc. A virtual private network (VPN) is typically set up across each WAN connection for security. Consequently, the SD-WAN can be an overlay spanning a diverse communications infrastructure.
Dynamic path selection
Another feature of SD-WAN is dynamic path selection—the ability to automatically and selectively route traffic onto one WAN link or another depending on network conditions or traffic characteristics. Packets may be steered onto a particular link because another link is down or not working very well, or to balance network traffic across all available links. SD-WAN can also identify packets by application, user, source/destination, etc. and send them down one path or another based on those characteristics.
Policy-based management
Policy is what determines where dynamic path selection will steer traffic and what level of priority (quality of service, or QoS) it is given. Business intentions can be implemented as policies via the central management console. New and updated policies are translated into operational rules and downloaded to all SD-WAN gateways and routers under control.
A policy may be created, for example, to ensure the best performance for VoIP and interactive web conferences by giving their packets transmission priority and routing them onto low-latency paths. Cost savings can be realized by sending file back-ups across a broadband Internet connection. WAN traffic that requires a high level of security can be restricted to private connections (e.g. MPLS) between sites and required to pass through a robust security stack when entering the enterprise.
Service chaining
An additional characteristic of SD-WAN is the ability to chain it together with other network services. WAN optimization (acceleration) is often combined with SD-WAN to improve network and application performance. Internet traffic leaving and entering a branch office may be routed across a VPN to a cloud-base security service to strike a balance between performance, security, and cost.
What Problems Does SD-WAN Solve?
MPLS cost and constraints
Multiprotocol label switching (MPLS) has been the mainstay of WAN connectivity between enterprise sites for more than a decade. It delivers guaranteed bandwidth, predictable latency, and privacy. Unfortunately, MPLS is expensive and may not be obtainable in many geographic locations. MPLS is also not a practical means of cloud connectivity in most situations.
Broadband Internet, in contrast, costs much less than MPLS and is globally available. While Internet connectivity is not as reliable and latency can vary, the cost savings are compelling. Many organizations now use a hybrid-WAN blend of these transports in which the traffic of business-critical applications is sent via MPLS and all else is routed over broadband Internet.
Software-defined WAN makes it much easier to set up a hybrid-WAN and find the right balance between cost, reliability and performance for a diverse mix of application traffic. This is due in large part to the capabilities of policy-based management and dynamic path selection that are inherent to SD-WAN.
Managing complex networks
The simplicity of management that SD-WAN brings to complex networks is arguably of even greater importance than MPLS cost savings.
Network complexity is increasing due to many factors including the use of hybrid WANs and a growing dependence on cloud-based applications. Traditional methods of managing WANs cannot scaled to meet this added complexity.
Configuring routers and gateways on an individual basis using scripts and command line interfaces (CLIs) is inefficient and error-prone. Productivity is reduced further when an expert must travel to set up new equipment at a remote site. A reliance on outdated methods and technologies has made it difficult for many network teams to keep up with business demands.
SD-WAN helps IT get control of complex networks and respond faster to changing business needs. It starts with the ability to design, deploy, and manage new equipment from a central location. The work of a network engineer is essentially complete after the design phase. A new SD-WAN gateway can be shipped to a remote site and plugged in by someone with no IT skills. The gateway will be discovered and brought online automatically with zero-touch provisioning—a workflow orchestrated by the central SD-WAN controller.
SD-WAN equipment can be managed using business-aligned policies written by a network engineer. Operational rules are automatically generated and downloaded to all SD-WAN devices under management when a policy is created or modified.
Unpredictable performance of public networks
Performance uncertainty is an issue with dependence on the Internet and other public networks for WAN connectivity. The path that the network traffic takes across the Internet can be different for every transmission between a pair of source and destination devices. Latency may vary significantly as a consequence.
Bottlenecks can also develop along the network path due to time-of-day congestion and random factors that constrain bandwidth. This problem is especially common on the “last mile” of the network when using an Internet service without guaranteed bandwidth. Many IT organizations set up redundant connections and services at each Internet breakout point to minimize the risk of a last-mile bandwidth bottleneck.
SD-WAN monitors the health of each WAN link and can use dynamic path selection to steer traffic down the best available path at each moment. It can also discriminate between the traffic of applications or users such that the best connection is reserved for the most important traffic—say, VoIP or applications that handle business transactions. Lower-priority traffic, like file backups, can be routed onto a connection that is less reliable.
SD-WAN Benefits
Cost savings
SD-WAN makes it easier to move non-critical WAN traffic from private MPLS links onto lower-cost broadband Internet. Centralized, policy-based management lets a network engineer put more (or less) traffic on broadband links at any time without having to reconfigure routers and gateways on an individual basis.
Another area of cost savings is administration—especially network service and ongoing maintenance. Network experts need not travel to remote locations for SD-WAN deployments and they can get more done back in the office by using centralized, policy-based management.
Find out more about SD-WAN cost savings in our white paper, Measuring the ROI (Return on Investment) of SD-WAN >
Agility
Business is moving at a faster pace today than ever before. IT teams are being asked to roll out new services to support business initiatives on aggressive schedules. Fortunately, SD-WAN gives network engineers the agility to respond quickly to requests for new WAN services and make changes to existing services. Many tasks that formerly took hours or days to accomplish require only minutes to do with SD-WAN.
A second kind of agility that SD-WAN provides is real-time traffic management. SD-WAN gateways continuously monitor the health of each WAN link connected to them. Traffic is quickly rerouted when a link fails or becomes congested.
Application performance
Monitoring link health and redirecting traffic as needed improves application availability and performance in a broad sense. SD-WAN can also improve (or reduce) performance on a selective, application-by-application basis.
Deep packet inspection is used to identify the applications associated with WAN traffic. Business-aligned policies implemented by the network engineer determine which applications are given higher priority (QoS) and which paths their packets will flow onto. For example, policies can be implemented to send video traffic over the highest-capacity circuits; send software updates over Internet broadband circuits; or send all business traffic over secure VPNs.
Another way that SD-WAN improves performance for cloud-based applications is by making it easier to set up Internet break-outs at remote offices. Eliminating the need to backhaul traffic through a central point of Internet access can reduce latency and improve the user experience for SaaS and other cloud-based applications.
Speed of deployment
Setting up network technology and equipment at a new branch office is much easier with SD-WAN than with traditional routers and gateways. A network engineer designs the node at a central management console. Then an SD-WAN appliance is then shipped to the branch office and plugged in by someone with little or no IT skills. On power-up, the appliance joins the network and connects to the central SD-WAN controller, which provisions and configures the new equipment and then brings it online.
That’s it! SD-WAN with zero-touch provisioning—an automated workflow executed by the central controller—eliminates the need for an expert to travel to the branch site or set it up remotely via a command line interface.
Is SD-WAN Secure?
SD-WAN can increase your network security with encrypted network traffic, network segmentation, the use of a central provisioning system, increased visibility into the WAN, and optimized performance overall. Segmenting your network limits any attack damage to a manageable area. A central provisioning system provides a piece of software that controls all of the separate nodes interdependently which gives better communication and connection between your network, very different from the traditional WAN setup.
