Desktop Virtualization
VMware Desktop Virtualization Overview
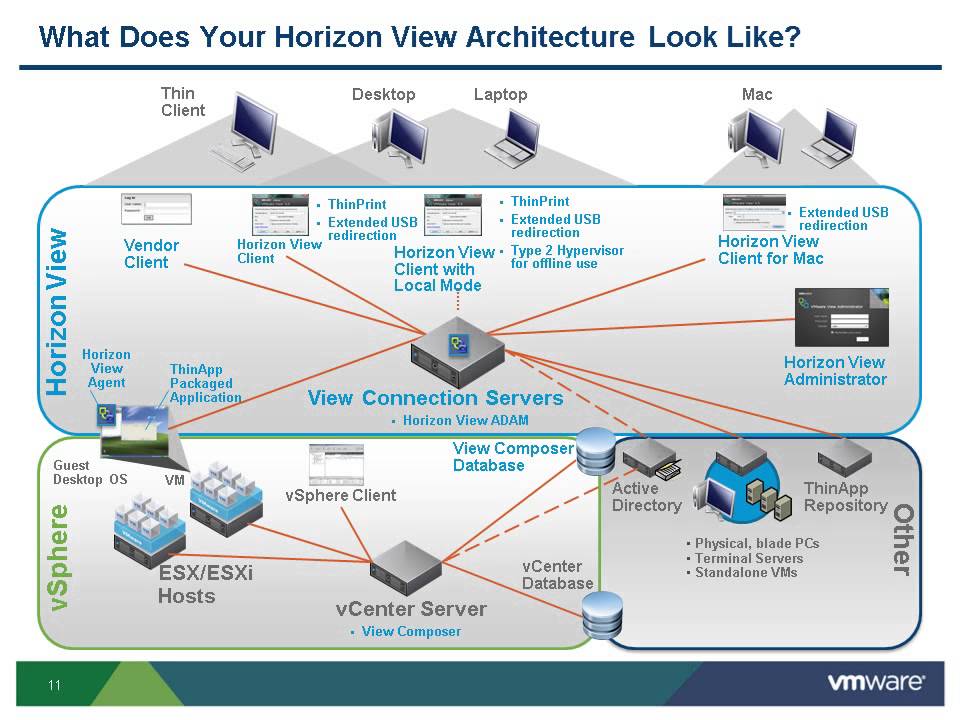
Virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) refers to the use of virtual machines to provide and manage virtual desktops. VDI hosts desktop environments on a centralized server and deploys them to end-users on request.
In VDI, a hypervisor segments servers into virtual mechines that in turn host virtual desktops, which users access remotely from their devices. Users can access these virtual desktops from any device or location, and all processing is done on the host server. Users connect to their desktop instances through a connection broker, which is a software-based gateway that acts as an intermediary between the user and the server.
VDI can be either persistent or nonpersistent. Each type offers different benefits:
- With persistent VDI, a user connects to the same desktop each time, and users are able to personalize the desktop for their needs since changes are saved even after the connection is reset. In other words, desktops in a persistent VDI environment act exactly like a personal physical desktop.
- In contrast, nonpersistent VDI, where users connect to generic desktops and no changes are saved, is usually simpler and cheaper, since there is no need to maintain customized desktops between sessions. Nonpersistent VDI is often used in organizations with a lot of task workers, or employees who perform a limited set of repetitive tasks and don’t need a customized desktop.
VDI offers a number of advantages, such as user mobility, ease of access, flexibility and greater security. In the past, its high-performance requirements made it costly and challenging to deploy on legacy systems, which posed a barrier for many businesses. However, the rise in enterprise adoption of hyperconverged infrastructure (HCI) offers a solution that provides scalability and high performance at a lower cost.
Benefits of VDI
Although VDI’s complexity means that it isn’t necessarily the right choice for every organization, it offers a number of benefits for organizations that do use it. Some of these benefits include:
- Remote access: VDI users can connect to their virtual desktop from any location or device, making it easy for employees to access all their files and applications and work remotely from anywhere in the world.
- Cost savings: Since processing is done on the server, the hardware requirements for end devices are much lower. Users can access their virtual desktops from older devices, thin clients, or even tablets, reducing the need for IT to purchase new and expensive hardware.
- Security: In a VDI environment, data lives on the server rather than the end client device. This serves to protect data if an endpoint device is ever stolen or compromised.
- Centralized management: VDI’s centralized format allows IT to easily patch, update or configure all the virtual desktops in a system.
